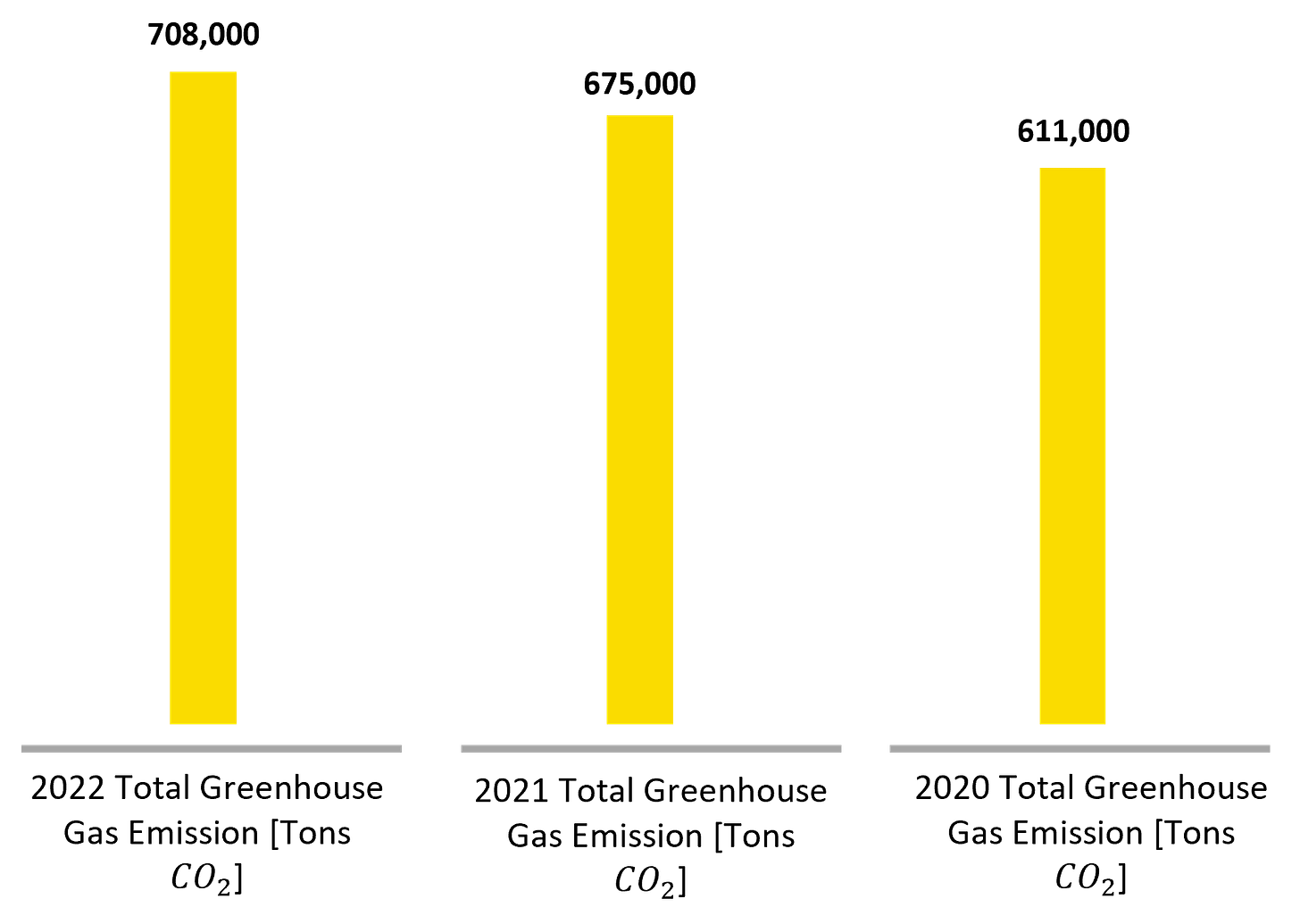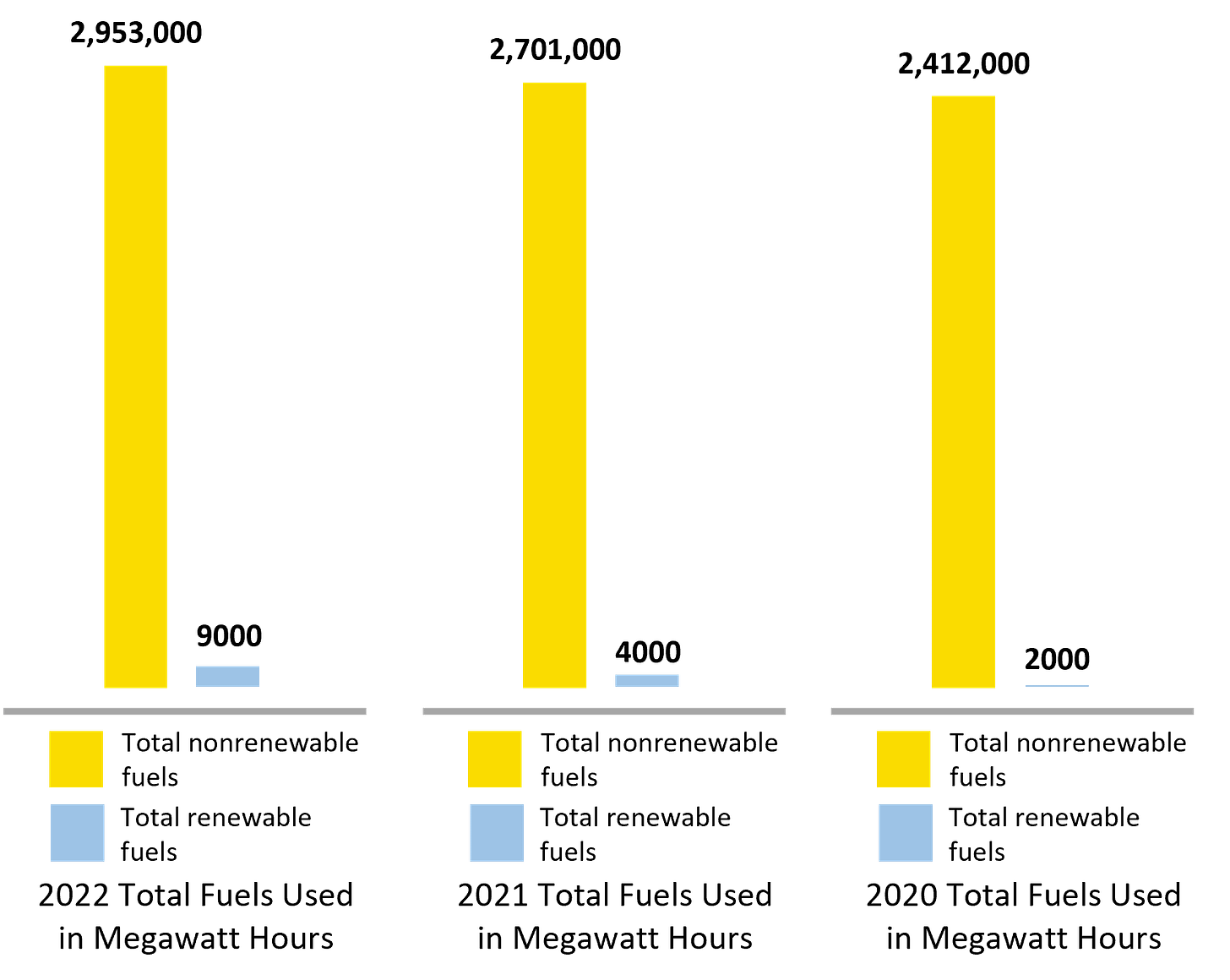What to know about Boeing in 2024: Navigating 737 MAX, Cost Cuts, Safety Challenges, and Sustainability Soars.
Is Boeing facing collapse? Not yet. Will they experience order losses and downsizing? Let's explore!

First things first, two weeks ago there were 0 subscribers. Today, there are 62 of us subscribing to this newsletter! Thank you to everyone who joined last week. We are 62 members strong, more than halfway to 100!
If you like this article, share it with your friends and family. If you DO NOT like this article, share it with your enemy.
Crafting this article took approximately 35 hours of dedication. While I provide it to you at no cost, the only favor I have is to share it within your network. Let's spread the message together!
Y’all are the best!
Join the story of Boeing, where uncertainties meet speculative possibilities in the dynamic world of aviation.
This journey isn't just about a company; it's a tale of technological progress, economic growth, and the environmental impact of a global industry.
Key Points
Navigating Boeing's Challenges: Boeing, facing a turbulent landscape, grapples with a series of setbacks, from the lingering repercussions of the 737 MAX crises to challenges with the 787 Dreamliner, 777X.
Boeing's Sustainability Commitments: Boeing's commitment to sustainability faces scrutiny as emission statistics reveal a 30% increase in fuel use, reliance on carbon offsetting, and potential pitfalls.
Safety vs Cost vs Sustainability Dilemma: The company grapples with safety challenges after a historical shift from engineering excellence to a cost-cutting culture.
The Paradox of Reduced Flights: Operational inefficiencies, including over 1.1 million affected passengers seeking alternative transportation weekly, and the use of passenger-free ferry flights highlighted the environmental toll of the unanticipated grounding.
The Human Element: Dave Calhoun, with unwavering transparency, admitted Boeing's "mistake" and emphasized a commitment to complete transparency in resolving the issue.
Conclusion - Is It the End of Boeing? Certainly, it is not the end of the aviation giant; rather, it signifies a very bumpy segment in their extensive journey.
Navigating Boeing's Challenges
In the turbulent landscape of aviation, Boeing, a stalwart in the industry, has weathered a series of setbacks in recent years. The narrative of Boeing's struggles extends beyond the well-documented grounding of the 737 MAX series, reaching into the heart of the company's engineering, production, and certification processes.
As we navigate through the timeline of Boeing's recent challenges, it becomes evident that the aviation giant faces not only the repercussions of past crises but also ongoing operational hurdles that shape its path to recovery.
737 MAX: A Legacy of Turmoil
The saga begins with the tragic incidents involving the Boeing 737 MAX, a series grounded globally in 2019 after the crashes of Lion Air Flight 610 in October 2018 and Ethiopian Airlines Flight 302 in March 2019. The accidents, attributed to a flawed Maneuvering Characteristics Augmentation System (MCAS) and inadequate pilot training, led to intense scrutiny of Boeing's engineering practices and the Federal Aviation Administration's (FAA) oversight.

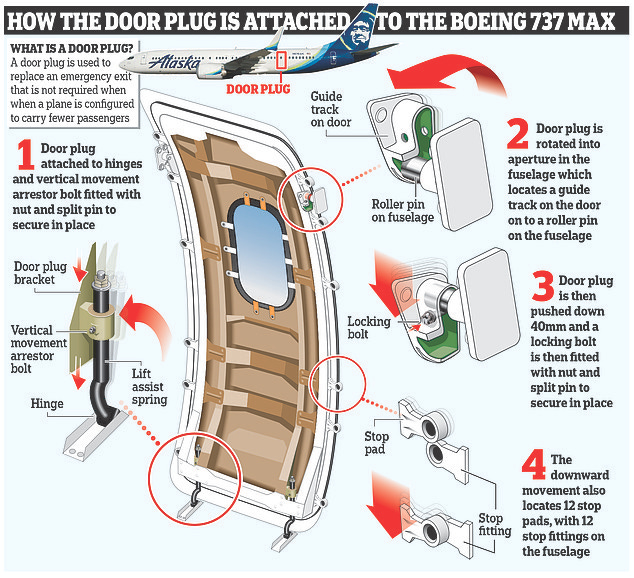
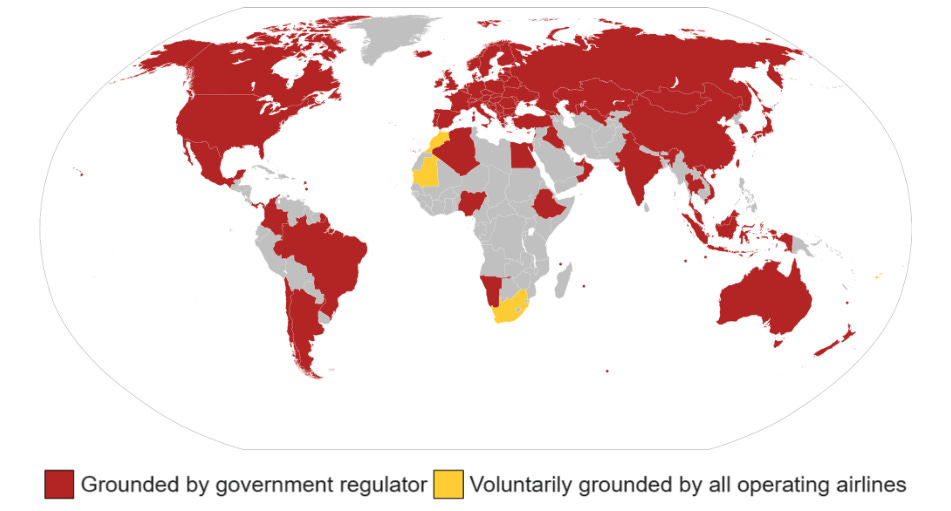
While the 737 MAX returned to service with safety enhancements, the story did not end there. Fast forward to 2024, and a new chapter unfolded with Alaska and United Airlines grounding its 737 MAX 9 fleet after a door plug blew out mid-air on January 5.
The FAA swiftly issued an emergency airworthiness directive (EAD), grounding the entire US 737 MAX 9 fleet. This incident, occurring just five days into the new year, crashed the entire Boeing CEO’s comeback plan for 2024. It is a reminder of the persistent challenges haunting the 737 MAX series.
Beyond the 737 MAX: A Mosaic of Issues
However, Boeing's turbulence extends beyond the troubled MAX series. The 787 Dreamliner, once a symbol of innovation, faced disruptions as inspectors discovered paper-thin gaps in its fuselage in 2019.
The subsequent grounding of eight planes and repeated pauses in Dreamliner deliveries piled up a backlog of orders reaching 2032 (assuming Boeing fulfills its commitment to doubling production by 2026). This occurred shortly after the same aircraft type faced issues with the Rolls-Royce Trend 1000 engine. Boeing is employing a meticulous approach to rebuild confidence in the Dreamliner program.
In 2021, a Boeing 777 planes powered by Pratt & Whitney engines experienced a harrowing engine failure, drawing attention to inadequate inspections and raising questions about the robustness of Boeing's safety protocols. Amid these incidents, Boeing navigates operational setbacks, such as the costly delays and financial losses associated with the Air Force's KC-46 Pegasus and the prolonged wait for the highly anticipated Boeing 777X, further challenging the company's resilience.
As we embark on a journey through Boeing's recent timeline, we unravel a complex narrative shaped by accidents, engineering flaws, and operational hurdles, underscoring the intricate task of steering an aviation giant through turbulent skies.
Boeing's Sustainability Commitments
In the complex world of aviation, safety is the top priority. Boeing, a major player in the industry, is dealing with the challenge of balancing safety and environmental responsibility. They've done tremendous job collecting and sharing sustainability data, presenting themselves as supporters of a greener aviation industry.
Yet, when we look deeper, there are specific measures that require careful consideration. Let's delve into how Boeing manages the complex relationship between safety and sustainability in an industry not known for strong environmental efforts.
Emission Statistics
Boeing places a pronounced emphasis on achieving net-zero carbon emissions from its manufacturing and worksites, a goal reportedly achieved in 2020. Yet, a deeper analysis of the numbers unveils a different story.
Recent years have seen a surge in emissions, questioning whether Boeing is really making big progress in sustainability. The surprising fact that the company now uses 30% more fuel than three years ago, along with the claim of zero carbon emissions, shows they depend on carbon offsetting.
Unveiling the Carbon Scam
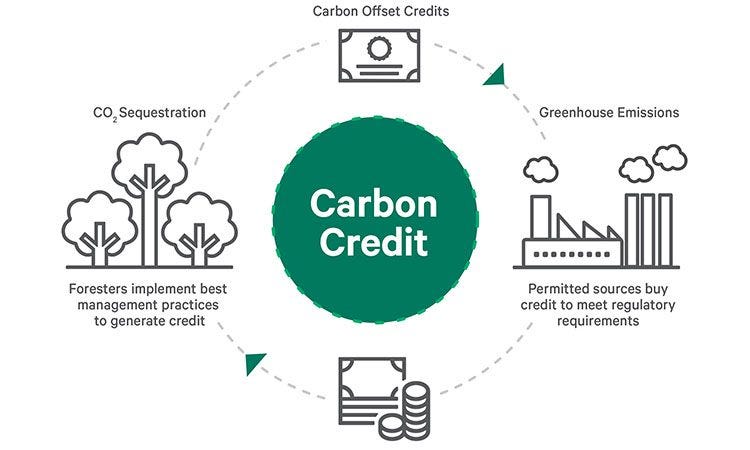
The widely embraced practice of carbon offsetting, including Boeing's participation, involves purchasing carbon rights from natural preserves and nature parks. Despite the seemingly noble intention of offsetting emissions, this practice often amounts to a green illusion.
By buying carbon rights, corporations claim to balance their carbon footprint while unwittingly burdening these preserves, and the environment at large, with the consequences of their activities.
Carbon credits enable corporations to expand their greenhouse gas emissions, raising questions about the efficacy of offsetting initiatives and the authenticity of corporate commitment to sustainability.
Innovative Tools for Emission Reduction
Boeing's commitment to sustainability extends beyond mere carbon emissions. In recent years, the company has spearheaded innovations that might escape the notice of the average passenger but play a pivotal role in environmental conservation.
Lower Emission Aircraft: Boeing's new airplanes boast significant efficiency gains, with each generation historically reducing fuel use and emissions by 15%-25%. Key advancements include the use of lightweight carbon-fiber composite materials on the 787, making it 30% lighter than aluminum traditionally used in aircraft construction. Winglets on planes like the 737 Max and 777X contribute to reduced drag, increased lift, and improved aerodynamics, resulting in a 5 - 7% reduction in fuel consumption.
Noise Reduction: Innovative engines, larger engine diameters, and improved fuselage acoustics contribute to a quieter and more environmentally friendly flying experience.
Waste Reduction: Boeing's implementation of the electronic flight bag (EFB) in 2023 marked a significant leap toward a paperless operation. This digital solution has saved approximately 5 billion sheets of paper, eliminating 14 million pounds of weight from planes and contributing to environmental conservation.
Renewable Energy Procurement
Boeing's strategic adoption of renewable energy sources, including solar, wind, and hydropower, reflects a commitment to reducing its carbon footprint. Beyond this, the company is exploring potential business diversification through sustainable aviation fuels (SAF).
Recognizing the industry's increasing shift away from fossil fuels, Boeing's collaboration with the United Arab Emirates (UAE) on alternative fuels, such as Power-to-Liquid (PtL), highlights a forward-thinking approach. PtL technology converts abundant solar and wind energy in the UAE into a liquid fuel. The successful Emirates flight test, utilizing 18 tons of SAF in one engine of a 777-300ER, underscores the feasibility and ambition of producing up to 70% of national jet fuel consumption from PtL SAF by 2050.
Boeing's journey toward sustainability, while marked by commendable efforts, prompts a critical examination of the strategies employed in navigating this intricate dance between safety and environmental responsibility.
Safety vs Cost vs Sustainability Dilemma
In the unfolding chapters of Boeing's aviation saga, the narrative takes a dramatic turn, underscoring the intricate dance between sustainability and safety. Once a stalwart in the aerospace industry, Boeing faced a crisis that reverberated through its very foundation, sparking a crucial dialogue about the equilibrium between sustainability and safety.
The recent cascade of incidents exposed chinks in Boeing's armor, laying bare the consequences of poor management and a lack of steadfast standards ingrained in the delicate relationship between leaders and shareholders. The ramifications of this shift, highlighted by the 737 MAX tragedies, underscore a pivotal moment in Boeing's narrative, prompting introspection on the high-stakes tightrope walk between sustainability aspirations and the uncompromisable pillar of safety.
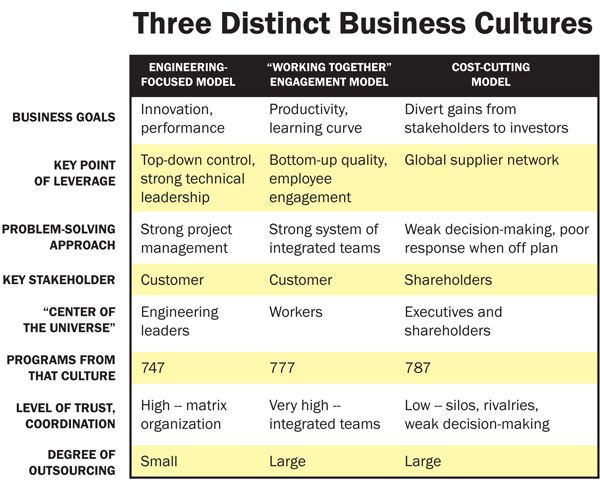
From Engineering Excellence to Cost-Cutting Culture
A significant cultural shift in the late '90s saw the emergence of a cost-cutting focus, prioritizing shareholder interests and short-term gains over the company's historical commitment to excellence.
The company stopped prioritizing intrapreneurial innovation and became the Amazon of aviation, producing airplanes just with an idea of corporate gains.
Not-so Green Sustainability Practices
2010s began a new era of eco conscious marketing practices. Boeing, in response to global trends started branding its more energy efficient aircrafts as eco-friendly, with 787 Dreamliner as a leader of a new eco-Dream. Positioning themselves as carbon-zero innovators, Boeing embraced practices like offsetting greenhouse gas emissions and investing in hydrogen-powered aircraft.
However, beneath the surface of this green facade lies a nuanced reality. While carbon offsetting has its merits, it often falls short of delivering the anticipated results. Boeing's sustainability practices, while contributing to a marketing narrative of environmental responsibility, also serve as a strategic tool to boost profits.
The emphasis on newer planes using less fuel is valid, but when considering the entire life cycle, including production burdens, technology implementation, and the waste generated by retiring old aircraft, the sustainability advantage of a new plane appears more marginal than the marketing spotlight suggests.
Cost-Cutting Measures Impact Safety
While retrofitting the old good 737 to 737 MAX, Boeing made several decisions dictated by cost-cutting pressure, that as latter reveled, might have lied at the foundation of the recent accidents. Boeing decided to reuse the well-known 737 structure while creating 737 MAX.
The decision makers assumed that the new airplane will not require additional training from the crew, what lowers the cost of implementation and encourages potential customers to purchase their product.
The aviation producer decided to implement several new systems without mandating simulator training for pilots. It made craw unaware of the system's existence and how to handle its operation in case of an emergency. This cost-cutting measure, aimed at avoiding expenses associated with simulator training, turned out to have severe implications for safety.
The MCAS system, designed to address aerodynamic changes in the MAX model, became a central point of failure. It triggered a series of events that led to the tragic crashes in Indonesia and Ethiopia. Pilots, unaware of the software's existence and functioning, found themselves grappling with an invisible hand taking control of their aircraft.
In the pursuit of sustainability and profitability, it is crucial for industry leaders, regulators, and stakeholders to collaborate in creating a robust framework that prioritizes safety without compromising efficiency. Only through a collective commitment to transparency, accountability, and stringent safety measures can the aviation industry truly soar to new sustainable heights.
The Paradox of Reduced Flights
Unintended Consequences of Grounded Skies
The grounding of all 387 Boeing 737 MAX planes by March 18, 2019, had a ripple effect across the aviation landscape, impacting 8,600 weekly flights operated by 59 global airlines. Surprisingly, the expectation of reduced greenhouse gas emissions due to fewer planes in the skies was countered by unintended consequences.
The Boeing 737 MAX, with its approximately 14% lower CO2 emissions compared to its predecessor, contributed to a greener footprint when operational. However, the grounding forced airlines to fill the void left in their operations, leading to a series of challenges:
Aging Fleet Efficiency:
Increasing reliance on older planes, which typically feature less fuel-efficient engines and technologies, resulted in an overall decrease in fuel efficiency for affected airlines.
Maintenance Challenges:
Older aircraft, now more prominently in service, demanded frequent and extensive maintenance. This uptick in maintenance activities translated to increased fuel consumption, countering the expected environmental benefits.
Ferry Flights and Operational Inefficiencies:
The disruption caused by the grounded planes, impacting 8,600 weekly flights globally, led to a cascade effect. With an average capacity of 165 passengers per 737 MAX, over 1.1 million individuals had to alter their plans weekly, seeking alternative transportation.
The aftermath witnessed several instances of ferry or logistical flights, undertaken post-grounding. These passenger-free flights, though not uncommon, contributed to fuel consumption without the transport of a single soul, highlighting the environmental toll of the unanticipated grounding.
The Human Element: Dave Calhoun's Perspective
“The culture of poor quality is generated from the top. Driving production numbers up and compromising on cost and quality. Calhoun knows this from his days at GE and he needs to take responsibility. Thank goodness he doesn't have to live with even more deaths caused by Boeing incompetence”.
Dave Calhoun takes center stage, representing Boeing.
In the aftermath of the Alaska Airlines incident, Boeing CEO David Calhoun addressed the company's staff in a pivotal "safety meeting" acknowledging the gravity of the situation and the company's accountability. Calhoun admitted Boeing's "mistake" and emphasized a commitment to complete transparency in resolving the issue, ensuring a thorough investigation with the National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB).

In this situation, Boeing finds itself cornered, with no room to evade the pressing issues. The only prudent course of action to rebuild customer and user trust is through complete honesty and transparency.
In the meeting held at the 737 factory in Renton, Washington, Calhoun took a moment to commend the crew of Alaska Airlines Flight 1282 for their exceptional handling of the emergency.
While addressing the potential manufacturing supply chain issue, Calhoun emphasized the imperative for a thorough investigation with the NTSB to pinpoint the root cause. Boeing, caught off guard, had limited time to devise a plan and determine their approach to the unfolding events. Even if the mistake stems from cost and quality-cutting measures, the company aims to present it in a manner that minimizes potential damage.
Boeing's commitment to complete transparency and collaboration with regulatory bodies, such as the NTSB, was a recurring theme throughout the meeting, echoing a dedication to openness in handling safety concerns.
In addition to tackling safety concerns head-on, Calhoun acknowledged the crucial role of communication in the aftermath of such incidents. Just a day after the accident, Boeing took proactive steps by creating a dedicated website tab and email address solely for addressing the incident.
This demonstrates their willingness to engage with the public. It appears as a strategic effort to guide and control the narrative, preempting speculations. This astute move positions Boeing to influence and shape the conversation in their favor.
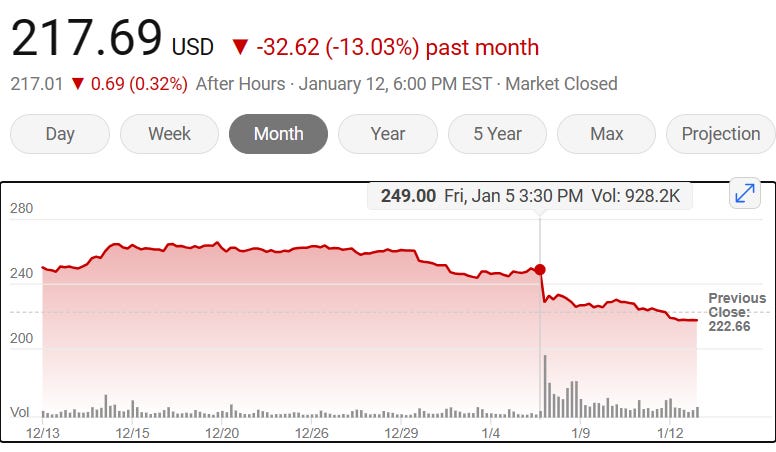
The stock market responded promptly, witnessing a sharp decline in Boeing's stock price from $249 to $217 per share. The incident has not only triggered Wall Street but has also garnered attention from lawmakers. Senator J.D. Vance called for a Senate Commerce Committee hearing to evaluate incidents involving the 737 MAX, examining Boeing's engineering and safety standards, along with the oversight provided by regulatory agencies.
President Joe Biden, closely tracking the situation, highlighted the grounding of Boeing 737 MAX 9 planes for inspection, emphasizing the importance of enhanced inspections before the aircraft is deemed airworthy. The White House expressed relief that all passengers and crew of Alaska Airlines Flight 1282 were safe and underscored the commitment to thorough investigations before resuming operations.
As Boeing faces this critical juncture, the human element takes center stage, with Dave Calhoun's perspective reflecting a commitment to transparency, safety, and collaboration in navigating the challenges posed by the recent incident. The ongoing investigations will shed light on the specific details, but Boeing's commitment to addressing the human and safety aspects remains unwavering.
Navigating Boeing's Future: Sustainability Outlook
As the aviation giant charts its course forward, several key areas demand attention and adaptation for a greener future.
Identifying Potential Areas for Improvement
Boeing must scrutinize its safety, cost management, and sustainability practices, starting with a comprehensive exploration of areas for improvement. This involves reevaluating aircraft design, fuel sources, and operational strategies to minimize environmental impact.
Speculating on the Future Trajectory
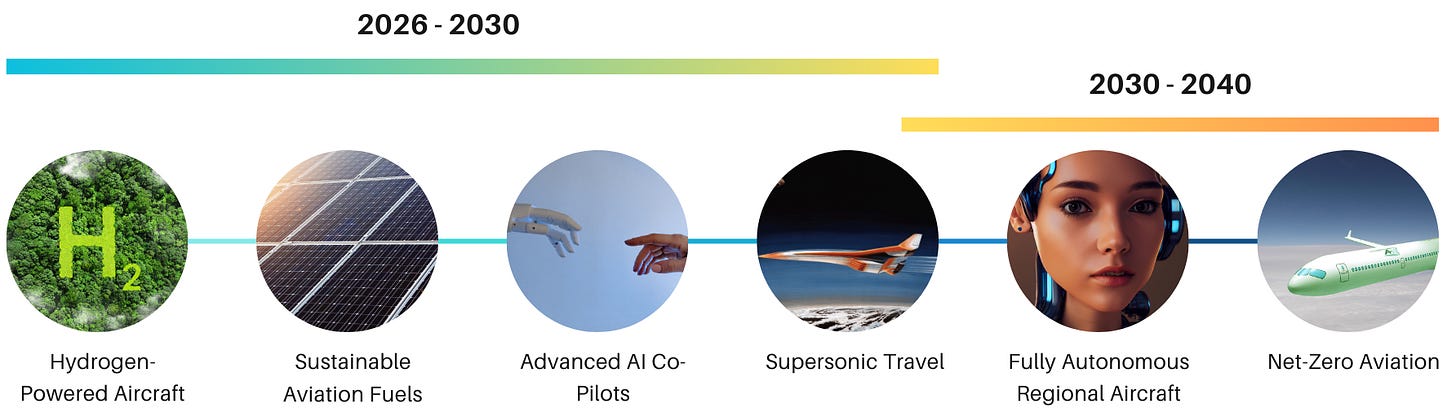
The mid-2020s could usher in transformative changes for Boeing and the aviation industry at large. The focus on sustainability might lead to the emergence of hydrogen-powered aircraft, supersonic travel, advanced AI co-pilots, and increased use of Sustainable Aviation Fuels (SAFs).
Hydrogen-Powered Aircraft: Hydrogen-powered planes may transition from theory to reality, promising a revolutionary shift in long-haul travel with substantially reduced greenhouse gas emissions. They are expected to move beyond theoretical discussions to practical prototypes and testing by 2026.
Supersonic Travel: Advancements in aerodynamics and engine technology could resurrect supersonic commercial flights, offering faster intercontinental travel with improved efficiency.
Advanced AI Co-Pilots: The integration of advanced AI in cockpits could enhance decision-making, data analysis, and routine tasks, contributing to safer and more efficient flights.
Sustainable Aviation Fuels (SAFs): Broader adoption of SAFs may become a norm, significantly reducing the carbon intensity of aviation operations.
2030s: Further Innovations
The mid-2030s might witness the aviation industry stepping into a new era with fully autonomous regional aircraft, and long-haul hydrogen-powered aircrafts.
Global Impact on Air Travel Patterns and Emissions
The evolving landscape of air travel extends beyond Boeing's boardrooms. Consideration of global shifts in air travel patterns and emissions, influenced by sustainable innovations, is crucial. How Boeing adapts may serve as a catalyst for broader industry changes.
In a rapidly changing aviation landscape, the transition towards sustainability is not just an option; it's an imperative. As Boeing navigates these challenges and opportunities, the entire industry watches, ready to follow the path towards a greener future.
Conclusion - Is It the End of Boeing?
Certainly, it is not the end of the aviation giant; rather, it signifies a very bumpy segment in their extensive journey.
Boeing's Challenges:
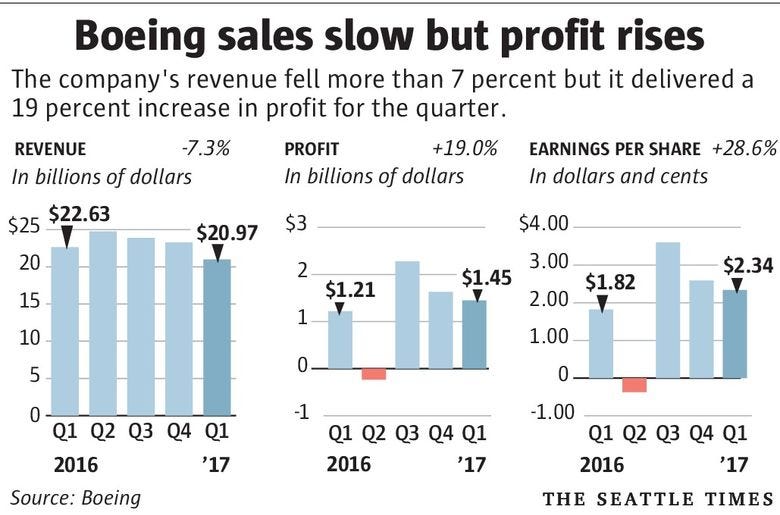
Financial Impact: The first 737 MAX crisis had significant financial repercussions for Boeing. The company faced substantial costs, including settlements, compensation to victims' families, and damage to its reputation. The total financial impact exceeded $20 billion. The recent Alaska Airlines accident added fire to the flames, possibly worsening their financial situation.
Order Cancellations and Delays: In the wake of the 737 MAX crisis, Boeing faced a turbulent period with substantial financial setbacks and a dent in its reputation. However, amid these challenges, the company found resilience in the loyalty of major clients, including industry giants like United Airlines and Ryanair. Why?
Operational Efficiency: United Airlines, Ryanair, and similar major clients opted to remain loyal to Boeing. The decision was grounded in operational efficiency, recognizing that maintaining a streamlined fleet from a single producer aligns with their financial objectives.
Cost Considerations: For these airlines, the financial calculus favored continuity with Boeing. Introducing a different aircraft type would necessitate extensive changes in operational procedures and pilot training processes. The cost implications of such transitions often outweighed the advantages of diversifying their fleet.
Boeing’s Strategy
Diverse Portfolio: Boeing's diverse portfolio, extending beyond the 737 MAX, played a crucial role in retaining key clients. The company's offerings, such as the 777 and 787 models, provided alternatives that met the varying needs of different airlines. Additionally, Boeing is involved in defense, space, and services sectors, providing some stability.
Adapting to Feedback: Boeing's response to the crisis involved a commitment to address shortcomings. The company's efforts to enhance safety measures and rebuild trust contributed to the decision of major clients to stay within the Boeing ecosystem.
Sustainability: Boeing has strategically embraced sustainability as a cornerstone for fostering trust and attracting new clients. The development of fuel-efficient aircraft, such as the 787 Dreamliner, not only aligns with global environmental initiatives but also positions Boeing as a leader in sustainable aviation. This commitment to eco-friendly solutions serves as a compelling strategy to resonate with environmentally conscious airlines and partners seeking to align their operations with a greener future.
Rebuilding Reputation: Boeing's ability to recover hinges on rebuilding its reputation for safety and reliability. The company has implemented changes in its management and processes to address the flaws that contributed to the 737 MAX incidents.
In essence, Boeing's story reflects an industry at the crossroads of challenges and opportunities, where the decisions and innovations made today will shape the future of air travel. As uncertainties persist, Boeing stands as a symbol of resilience, adapting to change and striving to redefine its path in a rapidly evolving aviation landscape.